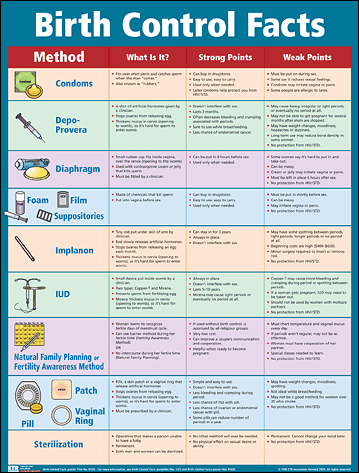
When it comes to family planning and preventing unwanted pregnancies, birth control options play a crucial role. With various methods available, it’s important to understand the ABCs of birth control to make an informed decision about which options suit your needs best.
A – Abstinence
Abstinence refers to abstaining from sexual activity altogether. It is considered the most effective method of birth control as it eliminates any risk of pregnancy. While abstinence may be the right choice for some individuals, it may not be practical or realistic for everyone.
B – Barrier Methods
Barrier methods, such as condoms and diaphragms, work by creating a physical barrier between the sperm and the egg. Condoms not only provide protection against unintended pregnancies but also prevent the transmission of sexually transmitted infections (STIs). Diaphragms, on the other hand, are inserted into the vagina to cover the cervix and block sperm from entering.
C – Combination Pill
One of the most commonly used methods of contraception, the combination pill contains synthetic hormones that prevent ovulation, thicken cervical mucus, and thin the uterine lining. This pill must be taken every day at the same time, and the combination of hormones ensures maximum effectiveness.
D – Depo-Provera Shot
The Depo-Provera shot is a form of progestin-only birth control that is administered every three months by a healthcare professional. It works by preventing ovulation and thickening cervical mucus. One of the advantages of the shot is that it doesn’t require daily maintenance like pills, making it suitable for individuals who prefer a longer-acting method.
E – Emergency Contraception
Emergency contraception, commonly known as the “morning-after pill,” is a method used after unprotected sex or contraceptive failure to prevent pregnancy. It contains higher doses of hormones than regular birth control pills and must be taken within a specific timeframe after intercourse.
F – Fertility Awareness-Based Methods
Fertility awareness-based methods involve tracking changes in your body to determine when you are fertile or infertile. This method requires diligently monitoring your menstrual cycle, basal body temperature, and cervical mucus. It is crucial to note that this method is most effective when used consistently and correctly.
G – IUD (Intrauterine Device)
An IUD is a small, T-shaped device that is inserted into the uterus by a healthcare professional. There are two types of IUDs – hormonal and non-hormonal. Hormonal IUDs release progestin, preventing pregnancy by thickening cervical mucus and suppressing ovulation. Non-hormonal IUDs contain copper, which creates an environment toxic to sperm, preventing fertilization.
H – Hormonal Implants
Hormonal implants are a long-acting, reversible birth control option that involves a small rod being inserted under the skin of the upper arm. It releases progestin to prevent pregnancy by stopping ovulation, thickening cervical mucus, and thinning the uterine lining. The implant can last for several years, providing an effective and low-maintenance contraception method.
I – Irreversible Sterilization
Irreversible sterilization methods, such as tubal ligation (for women) and vasectomy (for men), are permanent birth control options. Tubal ligation involves the blocking, sealing, or cutting of the fallopian tubes, while vasectomy involves cutting or blocking the vas deferens. These procedures are considered irreversible and should only be chosen if you are absolutely sure you do not want to have children in the future.
J – Juxtaposing Multiple Methods
Some individuals choose to utilize multiple birth control methods simultaneously to enhance effectiveness and provide additional protection against unintended pregnancies. For example, combining condom usage with a hormonal method like the pill or an IUD can offer dual protection against pregnancy and STIs.
K – Keep a Healthcare Provider in the Loop
It is essential to consult with a healthcare provider when considering birth control options. Each person’s needs are unique, and a healthcare professional can guide you towards the most suitable options based on your medical history, lifestyle, and goals.
L – Long-Term Reversible Contraceptives
Long-term reversible contraceptives, such as IUDs, hormonal implants, and contraceptive injections, provide effective protection against pregnancy for an extended period. If you’re looking for an option that does not require daily attention, these methods may be worth considering.
M – Male Condoms
Male condoms are thin sheaths made of latex or polyurethane that are worn over the penis during sexual intercourse. They are an effective barrier method, providing a physical barrier that prevents sperm from reaching the egg. Male condoms are easily accessible, inexpensive, and also protect against STIs.
N – Natural Family Planning
Natural family planning, also known as the “rhythm method” or “fertility awareness,” involves tracking the menstrual cycle and avoiding intercourse during fertile periods to prevent pregnancy. While this method can be highly effective when practiced correctly, it requires discipline, consistency, and accurate monitoring.
O – Over-the-Counter Options
Several birth control options, such as male and female condoms, emergency contraception, and spermicides, can be purchased over-the-counter without a prescription. These options provide accessibility and convenience for individuals seeking immediate solutions.
P – Patch
The birth control patch is a small adhesive patch that contains synthetic hormones similar to those in combination pills. It is applied to the skin once a week for three weeks, followed by a patch-free week to allow for menstruation. The patch is a discreet and easy-to-use option, providing effective contraception when used correctly.
Q – Quality Matters
When it comes to birth control, quality matters. Ensure that you purchase products from reputable sources and follow instructions carefully. In the case of prescribed contraceptives, consult with a healthcare provider to ensure you are receiving genuine medications that will provide the intended protection.
R – Ring
The birth control ring, also known as the vaginal ring, is a flexible, transparent ring that is inserted into the vagina once a month. It slowly releases hormones to prevent pregnancy by inhibiting ovulation, thickening cervical mucus, and thinning the uterine lining. It offers a convenient and effective contraceptive option.
S – Spermicides
Spermicides are chemical substances that come in various forms such as gels, foams, creams, or suppositories. They work by immobilizing or killing sperm, providing an additional barrier method when used with condoms or diaphragms. However, spermicides alone are less effective at preventing pregnancy compared to other methods.
T – Timing is Everything
Timing is essential when it comes to birth control. Certain methods, such as the pill, patch, ring, or injections, require strict adherence to specific timing to maximize effectiveness. Make sure to read and follow the instructions carefully to ensure optimal protection.
U – Under the Guidance of Healthcare Professionals
Consulting with healthcare professionals ensures that you receive accurate information, guidance, and recommendations tailored to your individual needs. They can help you navigate through the numerous options available, take into account any underlying medical conditions, and assist in finding the best birth control method for you.
V – Vasectomy
Vasectomy is a permanent form of male sterilization that involves cutting or blocking the vas deferens, preventing sperm from entering the semen during ejaculation. It is a relatively simple surgical procedure, but, like any permanent decision, it should be made after careful consideration and discussion with a healthcare professional.
W – Withdrawal Method
The withdrawal method, also known as “pulling out,” involves withdrawing the penis from the vagina before ejaculation. However, this method is highly unreliable as pre-ejaculate fluid may contain sperm, increasing the risk of pregnancy. It offers no protection against STIs and is generally not recommended as a primary birth control method.
X – Xenodochial Advice
Seek advice from trusted individuals, support groups, online communities, or healthcare professionals when considering birth control options. Hearing about personal experiences, research, and getting recommendations can help you make informed decisions and find the method that best aligns with your needs and preferences.
Y – You Are in Control
Remember that you are in control of your reproductive health. Explore the available options, educate yourself, and prioritize your well-being. Not all contraceptives work the same for everyone, so take the time to find what suits you best.
Z – Zero Judgement
Lastly, remember that the choice to use birth control is a personal decision, and there should be zero judgment. Everyone’s circumstances, beliefs, and objectives are unique. Respect and support others’ choices while advocating for comprehensive access to birth control options for all.
Now armed with the ABCs of birth control options, you can confidently navigate through the vast array of choices available. Each method has its advantages and considerations, so take the time to explore and find the one that aligns with your lifestyle and preferences. Remember, birth control empowers you to take charge of your reproductive health and make informed decisions about family planning.