The prostate is a small gland located below the bladder in men. It plays a crucial role in the reproductive system by producing fluid that nourishes and protects sperm. However, as men age, the prostate gland can become susceptible to various health issues, including prostate cancer, prostatitis, and benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH).
Risk Factors for Prostate Health
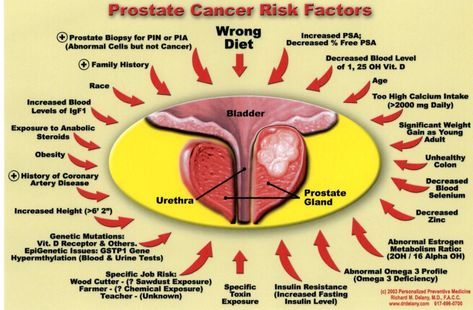
While the exact causes of prostate health problems are still unknown, there are several risk factors that may increase a man’s chances of developing these conditions:
Age: Prostate problems are more common in older men, with the risk increasing significantly after the age of 50.
Family History: Having a close relative, such as a father or brother, with prostate issues can elevate the risk.
Ethnicity: African-American men are more likely to develop prostate cancer compared to men of other races.
Diet: A diet high in red meat and low in fruits and vegetables can increase the risk of prostate-related conditions.
Lifestyle Factors: Lack of physical exercise, obesity, and smoking have also been associated with a higher likelihood of prostate health problems.
Prevention Tips for Prostate Health
Although the onset of prostate health issues cannot always be prevented, certain measures can be taken to minimize the risk:
Eat a Balanced Diet
Consuming a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can contribute to overall prostate health. Foods like tomatoes, broccoli, green tea, and fatty fish (such as salmon) that are high in antioxidants and omega-3 fatty acids have been linked to a reduced risk of prostate cancer.
Maintain a Healthy Weight
Being overweight or obese can increase the risk of prostate problems. Engaging in regular physical activity and adopting a lifestyle that helps maintain a healthy weight can have a positive impact on prostate health.
Be Active
Regular exercise, such as brisk walking, jogging, or cycling, can help reduce the risk of prostate issues. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity per week.
Quit Smoking
Smoking is not only detrimental to lung health but has also been linked to an increased risk of prostate problems. Quitting smoking can significantly improve overall health, including prostate health.
Screening and Early Detection
Regular prostate screenings are crucial for early detection of potential issues. Screening methods used to evaluate prostate health include:
Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA) Test: This blood test measures the level of PSA, a protein produced by the prostate gland. Elevated PSA levels may indicate prostate issues, although further evaluation is needed to confirm any abnormalities.
Digital Rectal Examination (DRE): During this physical examination, a doctor inserts a gloved finger into the rectum to check for any abnormalities in the prostate.
It is important to discuss the frequency and necessity of screening with a healthcare professional as recommendations may vary depending on individual risk factors and overall health. Early detection can significantly improve treatment outcomes and overall prognosis.
Conclusion
Understanding the risk factors associated with prostate health problems is essential for prevention and early intervention. By adopting a healthy lifestyle, maintaining a balanced diet, and undergoing regular screenings, men can take proactive steps to protect their prostate health and overall well-being.