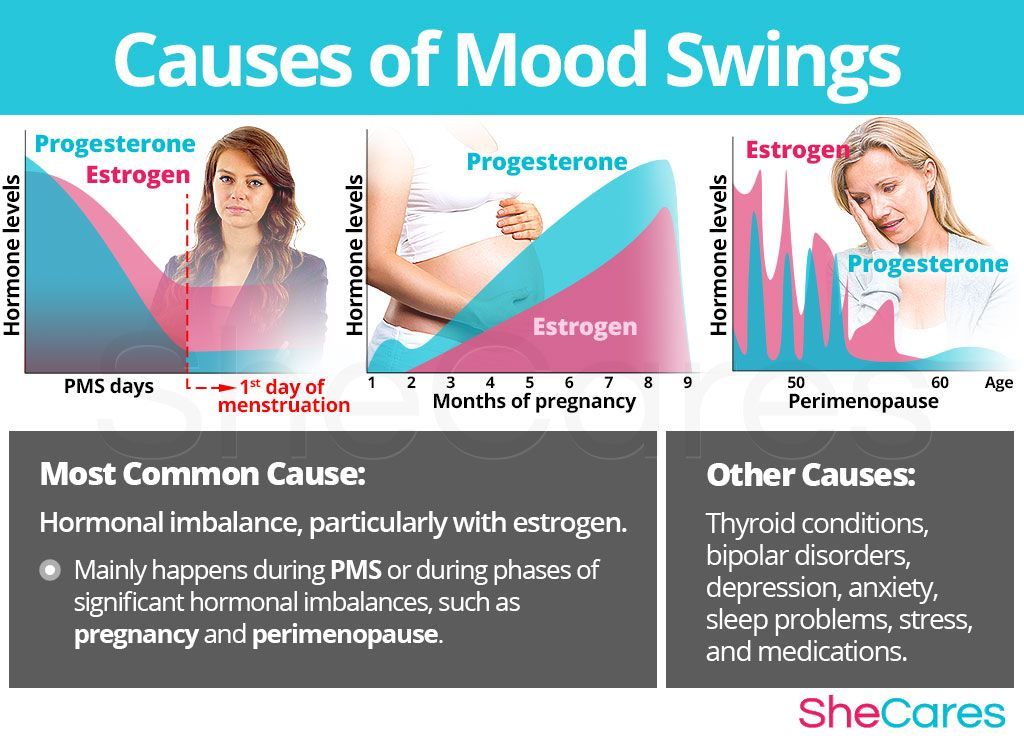
As women, our hormonal health plays a significant role in our overall well-being. Hormonal imbalances can often cause various health issues, such as premenstrual syndrome (PMS) and menopause. Understanding and managing these hormonal changes can greatly improve our quality of life.
Premenstrual Syndrome (PMS)
Premenstrual syndrome, commonly known as PMS, is a set of physical and emotional symptoms that occur about a week before menstruation starts. It is estimated that around 90% of women experience some degree of PMS during their reproductive years.
Common symptoms of PMS include mood swings, bloating, breast tenderness, fatigue, irritability, and food cravings. These symptoms can vary in severity from woman to woman, and even from cycle to cycle. The exact cause of PMS is still unknown; however, hormonal fluctuations, particularly a decrease in estrogen and progesterone levels, are believed to be major contributors.
Managing PMS involves adopting various lifestyle changes and seeking medical interventions, if necessary. Here are some strategies that may help:
Lifestyle Changes
Diet: Maintaining a balanced diet can significantly impact PMS symptoms. Incorporating whole grains, fresh fruits and vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats into your daily meals can provide essential nutrients and help regulate hormone levels.
Exercise: Regular physical activity, such as walking, swimming, or yoga, can help alleviate PMS symptoms. Exercise promotes the release of endorphins, which are natural mood boosters. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise on most days of the week.
Stress Management: Stress can worsen PMS symptoms. Engage in stress-reducing activities such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, or journaling. Finding healthy outlets for stress can make a significant difference in your overall well-being.
Medical Interventions
Over-the-counter Medications: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can help relieve menstrual cramps, breast tenderness, and other physical discomforts associated with PMS. Consult your healthcare provider for appropriate dosages and possible side effects.
Oral Contraceptives: Birth control pills that contain a combination of estrogen and progestin can help regulate hormone levels and reduce PMS symptoms.
Alternative Therapies: Some women find relief through alternative therapies such as acupuncture, herbal supplements, or biofeedback. While more research is needed to support their effectiveness, consult with a qualified practitioner before trying any alternative treatment.
Menopause
Menopause is a natural phase in a woman’s life when she ceases to have menstrual periods permanently. It typically occurs between the ages of 45 and 55, with the average age being 51. The transition into menopause, known as perimenopause, can last several years and can bring about a variety of physical and emotional changes.
During menopause, the body produces fewer hormones, particularly estrogen and progesterone, leading to various symptoms such as hot flashes, night sweats, mood swings, vaginal dryness, and sleep disturbances. Menopause can also increase the risk of osteoporosis and heart disease.
Managing menopause symptoms requires a holistic approach that focuses on overall health and well-being. Here are some strategies to consider:
Lifestyle Changes
Healthy Diet: A diet rich in calcium, vitamin D, and other essential nutrients can help combat the increased risk of osteoporosis during menopause. Additionally, consuming phytoestrogen-rich foods, such as soy products and flaxseeds, may help alleviate some menopausal symptoms.
Regular Exercise: Engaging in weight-bearing exercises, such as walking, dancing, or strength training, can help strengthen bones and reduce the risk of osteoporosis. Exercise also aids in maintaining a healthy weight and promoting better sleep.
Stress Reduction: High stress levels can exacerbate menopausal symptoms. Explore stress-relieving techniques, such as meditation, yoga, or tai chi, to promote relaxation and overall well-being.
Medical Interventions
Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT): HRT involves taking estrogen or a combination of estrogen and progesterone to alleviate menopausal symptoms. It is a highly effective treatment, but it carries certain risks and should be discussed with a healthcare provider to determine if it is suitable for you.
Non-hormonal Medications: Certain medications such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and gabapentin can help manage mood swings, hot flashes, and sleep disturbances. Discuss with your healthcare provider about the best options for your specific needs.
Vaginal Estrogen: Vaginal estrogen can help relieve vaginal dryness and discomfort associated with menopause. It comes in various forms, including creams, tablets, rings, or suppositories, and can be discussed with your healthcare provider.
Conclusion
Navigating hormonal changes during PMS and menopause can be challenging, but with the right knowledge and management strategies, it is possible to improve our hormonal health and overall well-being. Remember to consult with your healthcare provider for personalized advice and guidance based on your individual needs.